Table of Contents
M.2 and mSATA (Mini-SATA) are compact form factors for Solid State Drives. In electronics, form factor refers to the physical characteristics of the devices or components. So, M.2 and mSATA represent the physical dimensions of the SSDs. mSATA is an older form-factor which is rare to see these days. However, the M.2 is the evolved version of the mSATA.
The shift from mSATA to M.2 happened mainly because M.2 supported both SATA and high-speed PCIe interfaces. The NVMe drives conform to the M.2 form factor and use the PCIe lanes to communicate with the system. However, mSATA is limited just to the SATA interface. The core issue with mSATA was its design architecture which was focused just on the SATA. So, when engineers refined and improved the mSATA form factor, it replaced both the mSATA and mPCIe form factors. Interestingly, M.2 got its name from its dual support for both SATA and PCIe.
Enough about the history and formation of these form factors. Let’s discuss the real-world difference between M.2 and mSATA.
Understanding the M.2 Form Factor?
M.2 is a compact form factor used by devices such as SSDs, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth cards, RAID controllers, etc. The most popular adoption is with the SSDs. You can find two types of SSDs with the M.2 form factor i.e. M.2 SATA and M.2 PCIe NVMe. These both share the same physical characteristics but are different in the interface and performance. The M.2 SATA SSDs can look like an M.2 NVMe but is different in compatibility, price, performance, latency, and other specifications. But, because M.2 represents the physical parameters of these drives, we will have to discuss both of them.
M.2 form factor 5 main size variations which are as follows:
2230: 22 mm wide, 30 mm long.
2242: 22 mm wide, 42 mm long.
2260: 22 mm wide, 60 mm long.
2280: 22 mm wide, 80 mm long (the most common size of M.2 SSDs).
22110: 22 mm wide, 110 mm long (used in large storage SSDs)
Type of M.2 SSDs
In terms of interface, we can divide M.2 SSDs into two types i.e. SATA and NVMe. Let’s start with the M.2 SATA first.
1. M.2 SATA
M.2 SATA SSDs have the performance of the normal SATA 2.5” drive i.e. up to 600 MB/s. To distinguish the M.2 SATA SSDs and their ports from NVMe drives, the M.2 slots would have two different keyings. Most M.2 SATA drives will have two notches on both sides of their connectors called B+M Key. Some older versions can just have the B-Key or a notch on the right side of the M.2 SATA port or the left side of the SSD.
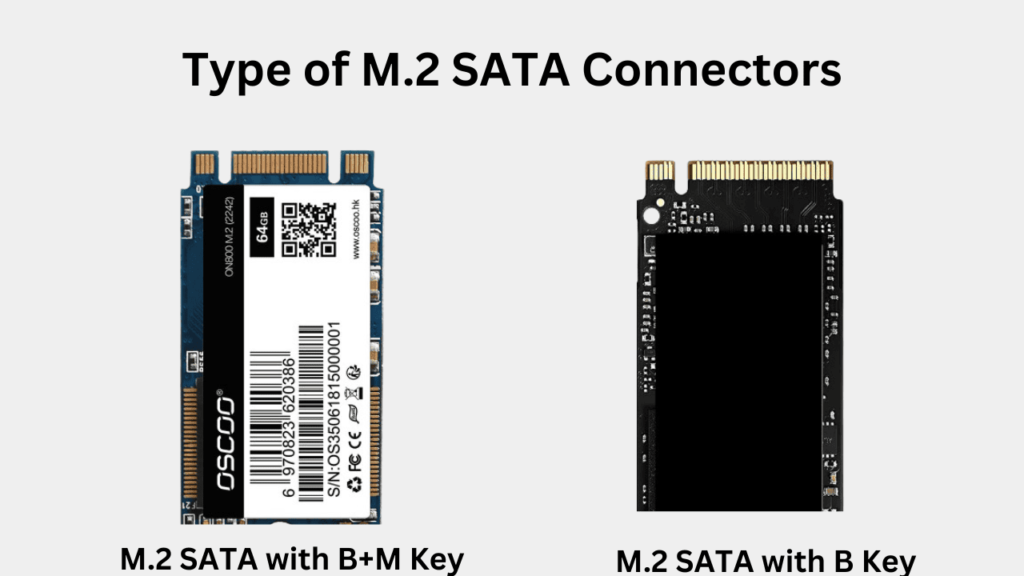
The M.2 SATA SSDs connect to the CPU through the SATA interface which is managed by the motherboard’s chipset. AHCI protocol is utilized to handle the transmission but because the SATA can’t be scaled after the SATA-3, the practical read/write performance can never go above 600 MB/s.
All the modern M.2 SATA SSDs will have both notches which makes these drives compatible with the M.2 NVMe ports as well. Yes, the M.2 NVMe ports support both NVMe and SATA SSDs. In fact, most modern computers will come with just the M.2 NVMe ports supporting any type of M.2 SSD. But, because M.2 SATA is limited by its design and interface, you can’t expect any performance benefits even when connecting to an NVMe port.
2. M.2 NVMe (PCIe)
Talking about the performance benefits, M.2 has a big contribution in allowing those high-speed NVMe drives to reach their full potential. M.2 helped a lot by bringing huge scalability and extensive physical and software support to the NVMe drives. M.2 NVMe SSDs use the PCIe interface to interact directly with the CPU. Generally, the SSDs would require 4 PCIe lanes of the same generation to offer its best performance. Because these lanes can be routed through the M.2 ports along with the traditional PCIe connectors, NVMe SSDs have a small form factor to work but with a very high bandwidth.

If we talk about the M.2 connector for NVMe SSDs, it has M-Key which means a notch on the right side. The best thing is that all NVMe SSDs will share the same connector type which makes it easier to buy our SSDs. On the software level, all NVMe drives are backward and forward-compatible, thanks to the PCIe interface.
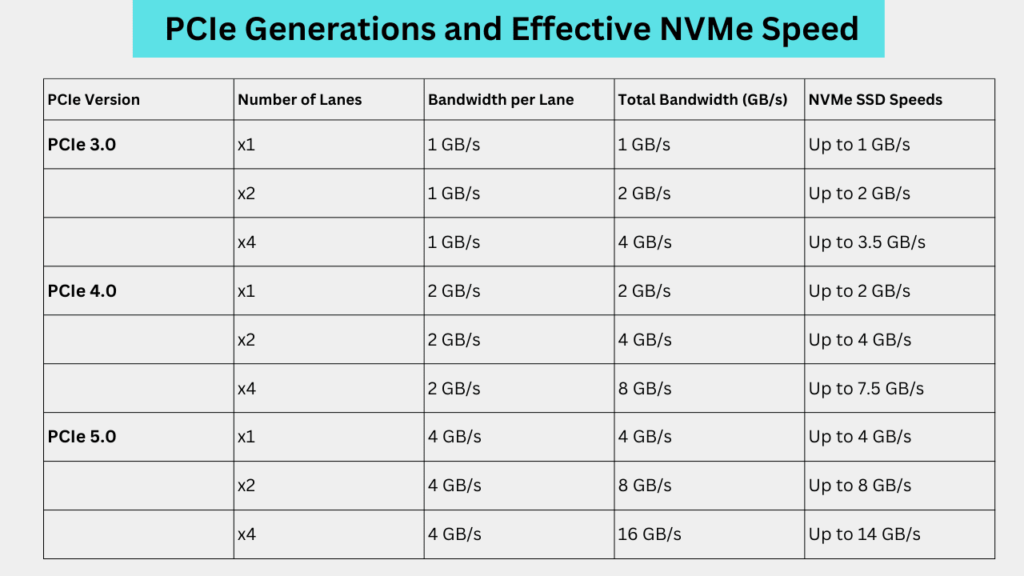
The latest and fastest generation of M.2 NVMe drives is the PCIe 5.0. However, the Gen 4.0 SSDs offer a good balance between performance and price. Now, different SSDs can give different speeds but the bandwidth is decided by the PCIe generation being utilized. Here is a table elaborating on the NVMe SSD performance based on its PCIe interface and allocated lanes.
Benefits of M.2 over mSATA
Because M.2 supports both SATA and NVMe, the need for the mSATA form factor is almost absolute. The low latency and high bandwidth of NVMe make the M.2 best not only for today but for future technologies as well. M.2 can also be utilized perfectly for Wi-Fi/Bluetooth cards in compact devices. The storage density can be huge with the help of 3D NAND. The NVMe drives have become a new standard in the computer hardware market and M.2 has allowed them to do this perfectly.
Understanding the mSATA Form Factor?
mSATA is another compact form factor based on the SATA interface as the name suggests. When it was launched, it came with numerous advantages compared to the traditional SATA drives. mSATA drives are compact in design and have lower power consumption. Also, because of the smaller size, they are more suitable for laptops. But, as we discussed above, the advent of the M.2 form factor, which was much more compact than the mSATA replaced it almost completely. However, you can still find some older laptops and desktops having support for mSATA SSDs.

mSATA only has one type of connector called a mini-PCIe connector. People generally confuse this form factor with the standard mini-PCIe connector but the mSATA connector supports just the SATA interface. While the connector may look like the ordinary mini-PCIe port, these both are electrically incompatible. In simple words, the mSATA SSD can go inside the mSATA port only. The mini-PCIe port can be used to install mini-PCIe cards, network cards, etc.
The key difference between mSATA and M.2
The biggest difference is that the M.2 is versatile, scalable, compact, and faster as compared to the mSATA. mSATA was a practical solution to save space and power during its time but today, M.2 has replaced it almost completely. mSATA was limited by the SATA interface which made it unsuitable for modern computers which require high data read/write performance. The performance that we see these days is achievable only with the PCIe interface. NVMe has its contributions to parallelism and latency reductions. But, the key benefit that M.2 offers is its great compatibility with the PCIe interface and the utilization of NVMe protocol. This allows for more adaptations like the SATA SSDs sharing the same M.2 form factor. But, still, M.2 NVMe is the most successful application of the M.2 form factor.
The downward trends of mSATA
You can still find the older systems, especially laptops with mSATA ports. But, M.2 has superseded mSATA for the good with its flexibility. Most laptops, desktops, and ultrabooks that were released after 2015 generally have M.2 ports (either SATA or NVMe). However, if your system is old, you may have to buy an mSATA SSD as well. The good thing is that we can buy them pretty easily at cheap prices. You can look at the OSCOO OM600 mSATA SSD if you need it for your system upgrade.
Conclusion
We can surely keep talking about the M.2 form factor and its benefits or applications in the current hardware industry. Being a trending form factor, it has got a lot of praise because of its good integration with SATA, PCIe, and NVMe interfaces. However, mSATA has done its job of providing a compact and efficient storage medium for the older system. It isn’t going to disappear from the markets anytime soon and there are systems still using the mSATA drives. M.2 and mSATA both have their benefits but M.2 has clearly got a lot of better things to offer and this is the reason it is the most popular form-factor in compact SSDs.