In 2025, artificial intelligence (AI) has moved beyond early-stage experimentation and initial rollout, entering a phase of broad application and large-scale industrial deployment. Whether it is the training of ultra-large-scale models or low-latency inference in business applications, AI’s usage scenarios and data volumes are growing explosively. This wave of growth is not only transforming the structure of compute resources but is also profoundly reshaping the storage layer’s demand profile—especially solid-state drives (SSDs). As a key component for data reading and persistence, SSDs are no longer just passive “capacity” modules; they are becoming critical system-level performance and intelligence elements.
The Background: How AI’s Scale-Up Drives Storage Demand
In recent years, the size of AI models and the compute required for training have grown at astonishing rates. According to the 2025 AI Index Report from Stanford HAI, the training compute of notable AI models has been doubling over ever-shortening time spans, and dataset sizes are also rapidly expanding, which means that training a large AI model now requires exponentially more storage, bandwidth, and persistence resources. More importantly, these large-scale models have moved from development environments into wide enterprise deployment and online inference scenarios, driving actual demand for low-latency, high-concurrency storage systems.
To put it into perspective: cloud training requires petabyte-level raw data and hundreds of terabytes to petabytes of model weights, while inference and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) scenarios introduce thousands of small random I/O requests and high concurrent reads. These trends challenge SSDs in ways simply increasing capacity cannot address.
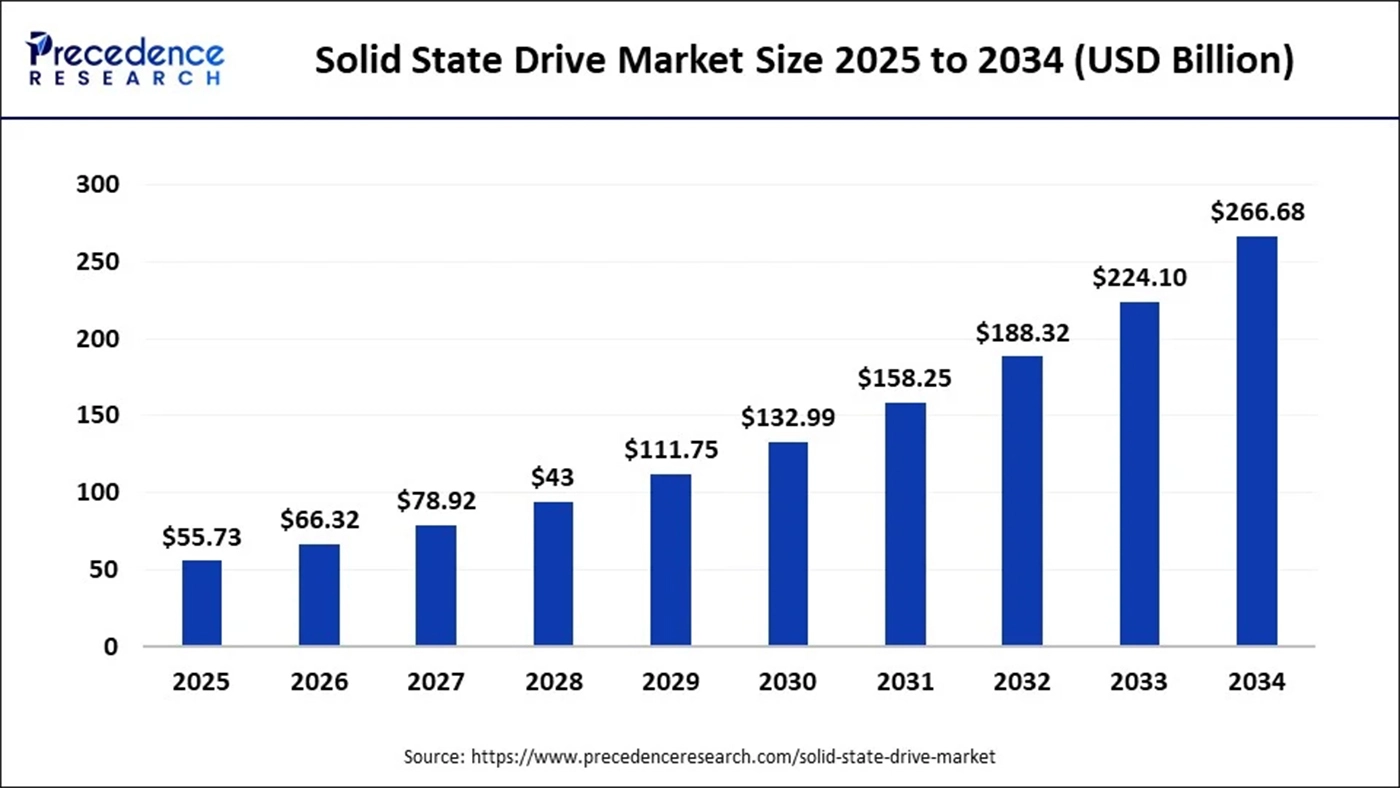
Meanwhile, market research firms’ forecasts for the SSD market reflect AI as a major growth driver. For instance, one forecast shows the global SSD market size in 2025 at approximately USD 55.73 billion, with projections climbing to around USD 266.68 billion by 2034.
This growth underlines that AI is raising both the demand for high-end SSDs and the bit-demand for NAND flash in general, which affects upstream supply-chain capacity planning and pricing.
On the supply side, memory vendors are increasingly aware of AI’s structural demands for high-bandwidth memory (HBM), DRAM and NAND. For example, a major memory vendor in 2025 declared that AI demand for HBM and other memory types is a key growth variable, indicating that memory and NAND supply chains are being impacted by AI projects that may take priority.
Additionally, the storage ecosystem around AI is forming new data architectures and service layers. Vector databases as core infrastructure for retrieval and semantic search have grown fast in 2024-2025, and their dependence on near-line storage (often NVMe SSD) underscores the increasing importance of SSD in the AI stack. Taken together, AI’s scale-up is not simply raising “capacity” demand—it is elevating requirements around performance (throughput, IOPS, latency), endurance (write durability), and intelligence (firmware and compute-enabled storage).
How AI Workloads Redefine SSD Technical Metrics
Traditionally, SSD selection has been a trade-off between capacity, cost per GB, and sequential read/write performance. But AI workloads bring new demands that make this triad insufficient.
In the training phase, storage demand emphasizes large capacity and high sequential throughput—but at the same time requires very high parallel bandwidth and persistent write capability. Training workflows involve frequent checkpoint writes, distributed saving of model slices, and massive sample data pre-processing—each of which impose heavy write throughput and endurance demands.
In online inference and RAG scenarios, SSDs face a different set of demands. These scenarios typically involve many small random reads with very low latency, especially when vector indexes or embeddings are sharded, and retrieval generates thousands of concurrent small random I/O requests. Low latency and high IOPS thus become critical for system response and user-experience. In many actual deployments, DRAM caching alone cannot cover the working set, making NVMe SSDs the necessary tier for near-line storage; the SSD must therefore maintain high random-read performance while balancing cost and capacity.
Moreover, in the AI lifecycle context, practices such as incremental checkpoints, fine-tuning of models, and parameter-server synchronization increase the frequency of writes and exacerbate write amplification. Thus, the endurance metrics (e.g., TBW, DWPD) of SSDs become more important than simply raw throughput. SSD vendors must adopt advanced Flash Translation Layer (FTL) algorithms, smarter garbage collection strategies, and more efficient write consolidation mechanisms to prolong lifespan and sustain performance.
From an overall system architecture viewpoint, interconnect technologies (e.g., PCIe 5.0/6.0, CXL) and distributed storage protocols (such as NVMe-oF) are becoming the backbone linking SSDs and compute nodes. Their higher bandwidth and lower communication overhead make storage access more efficient in large-scale training, which in turn pushes the role of SSDs in architecture: no longer merely a static data store, but a real-time data channel closely coupled with compute.
Technology Roadmaps: How SSDs Respond to AI’s New Needs
In response to the evolving demands, SSD vendors and system architects are following clear design directions. First, interface and protocol upgrades are foundational. PCIe 5.0 is already being adopted, and PCIe 6.0 is expected to be gradually launched over the next few years. Higher link bandwidth directly expands the maximum available throughput per drive and reduces reliance on many parallel drives, thereby increasing system integration flexibility.

In terms of NAND die choice, vendors must weigh cost versus performance. QLC and upcoming PLC multi-bit cell NAND, thanks to their lower cost and higher bit-density, are well suited for cold or “warm” data storage, supporting large-scale data economic retention. At the same time, SLC/MLC types—or higher-end enterprise-grade dies—remain essential for hot data requiring high IOPS and long life. Many vendors therefore add larger DRAM or SLC cache areas within SSDs and apply intelligent hot/cold tiering so that QLC can still perform acceptably in scenarios with heavy random writes.
Controller and firmware innovation become even more critical. Because AI scenarios impose more complex I/O patterns, traditional controllers may no longer suffice. More advanced controllers can perform smarter scheduling, embed acceleration (for example, compression/decompression, on-drive pre-filtering), and implement more complex FTL routines to optimize write consolidation and garbage collection, thereby reducing write amplification and improving endurance.
Another noteworthy development is “computational storage”—embedding specialized processing units inside the SSD so that some compute (e.g., feature extraction, vectorization, pre-filtering) can occur near the storage itself. For AI, this means that SSDs themselves can perform initial filtering or embedding generation, reducing data movement between host and storage and improving end-to-end efficiency. If this capability becomes standardized and software-ecosystem support matures, it could deeply reshape large-scale AI pipelines.
Beyond hardware and protocols, the way storage is integrated at the system level is also changing. For example, CXL (Compute Express Link) offers a way to more tightly couple memory and persistent storage, making memory or near-memory resources dynamically accessible across nodes—important when training large AI models with huge parameter volumes. If CXL becomes widely adopted, the positioning and required characteristics of SSDs may shift; in some cases, persistent memory (PMEM) or storage-class memory (SCM) could become viable, but due to cost and ecosystem maturity, NVMe SSDs are expected to retain dominance in the foreseeable future.
How Vector Databases, SDS and Data Governance Affect SSD Usage
Hardware lays the foundation, but the key is still how software leverages that hardware to serve AI pipelines. In recent years, vector databases, as the core of semantic search and RAG scenarios, have grown at a blistering pace in 2024-2025. These databases typically adopt a “DRAM + NVMe SSD” tiered storage architecture, keeping hot vectors in memory, and larger, near-line vector sets on NVMe SSD to balance cost and responsiveness. The rise of vector databases has directly increased NVMe SSD importance in retrieval scenarios and pushed vendors to optimize SSDs for random-read stability and low latency.
At the same time, software-defined storage (SDS) vendors are offering high-performance block storage services in cloud and private-cloud settings. SDS shines because it can orchestrate underlying SSD resources to provide QoS (quality of service), elastic scaling, and finer-grain hot/cold data tiering—very useful for platforms that need to handle training and inference workloads concurrently while controlling cost.
Another often overlooked dimension is data governance and versioning tools. In AI model workflows, numerous checkpoints and dataset versions (e.g., via DVC or similar tools) generate distinct write patterns. These include periodic snapshot writes, branching data sets, and audit logs—all of which lead to spikes in write loads. For SSD vendors and system architects, modeling these write curves and designing corresponding caching strategies becomes necessary to ensure the system can operate steadily over the long term.
Supply & Demand and Market Dynamics
The AI explosion is re-elevating memory and storage resources into spotlight, posing supply-demand balancing challenges for NAND flash. Industry reports and news articles indicate that memory vendors in 2025 are treating AI’s demand for HBM and other memory types as a key variable for revenue growth. Although HBM is more directly aimed at accelerators, the upward pressure on memory and NAND demand influences the cost structures and delivery timelines of SSDs.
From a market standpoint, SSD revenue forecasts show positive trajectories and an increasing share for enterprise-grade and AI-specific SSDs. For example, one forecast places the SSD market size at USD 55.73 billion in 2025, reaching USD 266.68 billion by 2034.
However, capacity expansion is capital-intensive and takes time; any mis-estimation in future demand can lead to oversupply or shortages, both of which cause price swings. These uncertainties mean industry participants must adopt more cautious planning. Further complicating this are global supply-chain risks—geopolitical tensions, raw-material price volatility, and the pace of equipment investment can all impact SSD release cycles and delivery performance. Vendors must balance R&D investment and capacity expansion: ensuring future product suitability for AI scenarios while avoiding the inventory burdens of over-capacity
Risks, Challenges and Three Key Future Watch-Points
When forecasting future developments, it’s critical to maintain sensitivity to uncertainties. First, standards such as CXL and PCIe 6.0 may take longer to achieve widespread adoption than expected; if their ecosystem matures slowly, the anticipated memory-storage decoupling may be delayed. Second, the actual deployment scale of computational storage remains to be seen; many scenarios involve migrating compute logic to SSDs, which demands full software-stack support and ecosystem coordination—this is not something hardware vendors can achieve alone. Third, alternative technologies (such as SCM, PMEM or other future non-volatile memories) may catch up in cost or performance with current NAND solutions, which would change long-term SSD demand profiles.
In addition, energy consumption and sustainability will become increasingly important. Large-scale training of GPT-class models plus massive SSD deployments can drive up data-center energy usage significantly. Beyond hardware efficiency, the industry needs to invest in metrics such as performance-per-watt and smarter scheduling to meet regulatory and enterprise ESG demands.
Timeline Overview: Key Milestones & Industry Evolution
| Time (Next 3 Years) | Key Event or Trend | Specific Impact on SSD Industry |
|---|---|---|
| 2024–2025 | Rapid growth of ultra-large scale model training and commercialization of vector databases | Drives demand for high-capacity NVMe SSDs and high-IOPS devices; in short term accelerates enterprise-grade SSD market expansion. |
| 2025 | Rising demand for HBM and high-bandwidth memory; some memory capacity prioritized by AI projects | Memory and high-end chip supply constraints may indirectly raise SSD costs and delay deliveries. |
| 2025–2026 | Wider deployment of PCIe 5.0; gradual establishment of PCIe 6.0 and CXL ecosystems | Increases maximum per-drive bandwidth and allows greater parallel data flow; supports more flexible storage architectures. |
| 2026–2027 | Trial and rollout of computational storage and SDS in some cloud or edge scenarios | If it delivers significant end-to-end bottleneck reduction, it will promote deeper storage-software co-innovation and reshape SSD positioning. |
SSD’s Role Is Shifting from “Carrier” to “Active Participant”
In summary, AI’s impact on the SSD industry in 2025 is already more than simply driving capacity expansion—it is a systematic shift touching performance metrics, controller/firmware innovation, software-ecosystem collaboration, and supply-chain realignment. SSDs are evolving from relatively passive hardware commodities into key components that actively participate in data-processing pipelines.
AI’s rise brings not only larger markets and higher revenue opportunities, but also deep introspection into the SSD design philosophy and industry collaboration models. Over the next three to five years, those who achieve breakthrough innovation in controllers, firmware, and software-defined storage will likely seize structural leadership in an AI-driven storage market. In a rapidly evolving technology and market environment, the combination of prudent yet proactive strategy, cross-ecosystem cooperation, and investment in long-term technical trends will be the key to success.